https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/21610
21610번: 마법사 상어와 비바라기
마법사 상어는 파이어볼, 토네이도, 파이어스톰, 물복사버그 마법을 할 수 있다. 오늘 새로 배운 마법은 비바라기이다. 비바라기를 시전하면 하늘에 비구름을 만들 수 있다. 오늘은 비바라기
www.acmicpc.net

풀이
격자마다 저장된 물의 양을 나타낼 int[][] map과 구름 위치를 저장할 큐 Queue<Pair> clouds를 생성한다.
Pair 클래스에 equals()와 hashCode()를 오버라이드한 이유는 이후에 설명하겠다.
static class Pair {
int x, y;
public Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Pair) {
Pair p = (Pair)o;
return p.x == this.x && p.y == this.y;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return x + y;
}
}
static int n;
static int[][] map;
static Queue<Pair> clouds = new ArrayDeque<>();
로직
1. 초기 구름 위치를 큐에 추가한다.
clouds.add(new Pair(n-2, 0));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-2, 1));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-1, 0));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-1, 1));2. 구름을 이동시킨다. 큐 사이즈만큼 큐에서 뽑고, 구름의 새로운 위치를 큐에 추가한다.
static void move(int d, int s) {
int size = clouds.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
Pair cloud = clouds.poll();
int x = cloud.x;
int y = cloud.y;
x += dx[d] * s;
y += dy[d] * s;
// n 이상인 경우
if (x >= n) x %= n;
if (y >= n) y %= n;
// 음수인 경우
while (x < 0) x += n;
while (y < 0) y += n;
clouds.add(new Pair(x, y));
}
}3. 구름이 있는 위치의 물의 양을 1씩 증가시킨다. 큐를 순회하면서 map[][]++한다.
4. 큐를 순회하면서 구름이 있는 위치마다 대각선 방향으로 거리가 1 있는 칸 중 물이 있는 칸 수만큼 물의 양을 증가시킨다.
static void increaseWaterWithCross() {
for (Pair cloud: clouds) {
int x = cloud.x;
int y = cloud.y;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dxd[i];
int ny = y + dyd[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && map[nx][ny] > 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
map[cloud.x][cloud.y] += cnt;
}
}5. map을 순회하면서 구름이 원래 있던 곳은 큐에서 제거한다. 원래 있던 곳이 아닌 곳 중 물의 양이 2 이상인 곳은 map[i][j] 값을 2 감소시킨 후 큐에 추가한다.
구름이 원래 있던 곳인지 구분하기 위해 clouds.contains() 메서드를 사용하였고, 같은 객체인지 확인하기 위해 Pair 클래스에 equals()와 hashCode()를 오버라이드하였다.
static void createNewCloud() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Pair p = new Pair(i, j);
if (clouds.contains(p)) {
clouds.remove(p);
}
else if (map[i][j] >= 2) {
map[i][j] -= 2;
clouds.add(new Pair(i, j));
}
}
}
}
코드
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static class Pair {
int x, y;
public Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Pair) {
Pair p = (Pair)o;
return p.x == this.x && p.y == this.y;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return x + y;
}
}
static int n;
static int[][] map;
static Queue<Pair> clouds = new ArrayDeque<>();
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1}; // 행
static int[] dy = {0, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1}; // 열
static int[] dxd = {-1, -1, 1, 1}; // 대각선 행
static int[] dyd = {-1, 1, -1, 1}; // 대각선 열
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
clouds.add(new Pair(n-2, 0));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-2, 1));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-1, 0));
clouds.add(new Pair(n-1, 1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int d = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
move(d, s);
increaseWater();
increaseWaterWithCross();
createNewCloud();
}
// 물의 총량 구하기
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
sum += map[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
static void move(int d, int s) {
int size = clouds.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
Pair cloud = clouds.poll();
int x = cloud.x;
int y = cloud.y;
x += dx[d] * s;
y += dy[d] * s;
// n 이상인 경우
if (x >= n) x %= n;
if (y >= n) y %= n;
// 음수인 경우
while (x < 0) x += n;
while (y < 0) y += n;
clouds.add(new Pair(x, y));
}
}
static void increaseWater() {
for (Pair cloud: clouds) {
map[cloud.x][cloud.y]++;
}
}
static void increaseWaterWithCross() {
for (Pair cloud: clouds) {
int x = cloud.x;
int y = cloud.y;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dxd[i];
int ny = y + dyd[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && map[nx][ny] > 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
map[cloud.x][cloud.y] += cnt;
}
}
static void createNewCloud() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
Pair p = new Pair(i, j);
if (clouds.contains(p)) {
clouds.remove(p);
}
else if (map[i][j] >= 2) {
map[i][j] -= 2;
clouds.add(new Pair(i, j));
}
}
}
}
}
참고
equals(), hashCode() 오버라이딩 참고 글
☕ 자바 equals / hashCode 오버라이딩 - 완벽 이해하기
equals 메소드 어떤 두 참조 변수의 값이 같은지 다른지 동등 여부를 비교해야 할때 사용하는 것이 equals() 메서드이다. 대표적으로 String 타입의 변수를 비교할때 가장 많이 거론되는 메서드일 것
inpa.tistory.com
다른 풀이
구름의 위치정보를 저장하는 자료구조로 Queue<Pair> 대신 2차원 배열 boolean[][] clouds를 생성한다.
로직 상 다른 부분
- move() 메서드 내에서 구름의 새로운 위치를 저장하는 2차원 배열을 따로 생성하고, 이후 clouds를 copyClouds의 값으로 업데이트해야한다.
참고: https://www.acmicpc.net/source/67735311
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] clouds;
static int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1}; // 행
static int[] dy = {0, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1}; // 열
static int[] dxd = {-1, -1, 1, 1}; // 대각선 행
static int[] dyd = {-1, 1, -1, 1}; // 대각선 열
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[n][n];
clouds = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
clouds[n-2][0] = true;
clouds[n-2][1] = true;
clouds[n-1][0] = true;
clouds[n-1][1] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int d = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
move(d, s);
increaseWater();
increaseWaterWithCross();
createNewCloud();
}
// 물의 총량 구하기
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
sum += map[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
static void move(int d, int s) {
boolean[][] copyClouds = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (clouds[i][j]) {
int x = i;
int y = j;
x += dx[d] * s;
y += dy[d] * s;
// n 이상인 경우
if (x >= n) x %= n;
if (y >= n) y %= n;
// 음수인 경우
while (x < 0) x += n;
while (y < 0) y += n;
copyClouds[x][y] = true;
clouds[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
clouds[i] = Arrays.copyOfRange(copyClouds[i], 0, n);
}
}
static void increaseWater() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (clouds[i][j]) {
map[i][j]++;
}
}
}
}
static void increaseWaterWithCross() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (clouds[i][j]) {
int x = i;
int y = j;
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = x + dxd[k];
int ny = y + dyd[k];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n && map[nx][ny] > 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
map[x][y] += cnt;
}
}
}
}
static void createNewCloud() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (clouds[i][j]) {
clouds[i][j] = false;
}
else if (map[i][j] >= 2) {
map[i][j] -= 2;
clouds[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
시간복잡도 차이
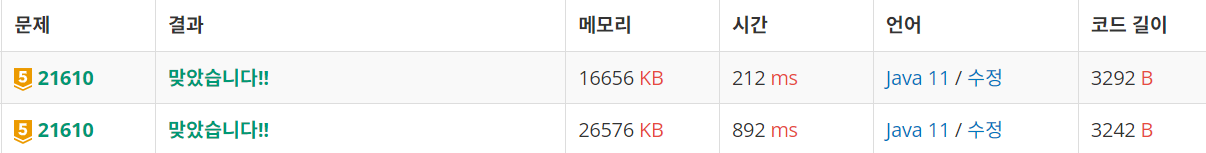
boolean[][]을 사용한 풀이는 시간복잡도가 O(m * n^2)이며, Queue<Pair>을 사용한 풀이는 시간복잡도가 O(m * n^3)이다. createNewClouds()메서드 내에서 사용되는 clouds.contains()의 시간복잡도가 O(n)이기 때문이다.
또한 Queue<Pair> 자료구조는 boolean[][] 배열보다 메모리를 더 사용한다.
따라서 시간복잡도와 메모리를 고려했을 때, Queue<Pair>보다 boolean[][]을 사용한 풀이가 더 효율적이다.
'Algorithm 문제 풀이 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 2503번 : 숫자 야구 - 자바[Java] (0) | 2023.10.13 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 20057번 : 마법사 상어와 토네이도 - 자바[Java] (0) | 2023.10.11 |
| [백준] 1916번 : 최소비용 구하기(다익스트라) - 자바[Java] (0) | 2023.10.04 |
| [백준] 15683번 : 감시 - 자바[Java] (0) | 2023.10.04 |
| [백준] 17140번 : 이차원 배열과 연산 - 자바[Java] (0) | 2023.10.04 |
